Introduction
In the previous article, we have seen how to call a stored procedure and map the native query result to POJO with Hibernate
In this article, we’re going to learn how to join unrelated entities with Spring Data JPA using JPQL and Hibernate using HQL.
HQL and JPQL
The Hibernate Query Language (HQL) and Java Persistence Query Language (JPQL) are both object model focused query languages similar in nature to SQL. JPQL is a heavily-inspired-by subset of HQL. A JPQL query is always a valid HQL query, but not vice versa.
Both HQL and JPQL are non-type-safe ways to perform query operations.
Domain Model
Assuming we have the following entities
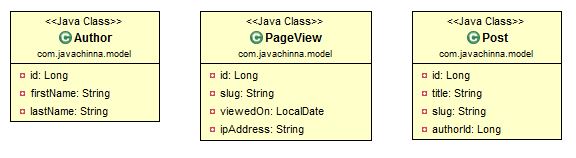
The Post entity has an authorId attribute which maps to the id attribute of Author entity.
The Post entity also has a slug attribute which defines the relative address of this particular HTTP resource on our application server. Every time a user visits a given web page, a PageView event is persisted with a slug attribute so that we know which web resource was viewed by the user.
Post and PageView has the slug attribute in common. Just because they share a common property, it does not mean that we need to define an association between these entities. However, we would still want to join them on a per-query basis.
Projections
Interface-based Projection
Spring Data JPA provides an interface-based projection. We need to declare an interface that exposes accessor methods for the properties to be read from the database.
PostWithAuthor.java
package com.javachinna.model;
public interface PostWithAuthor {
public Post getPost();
public Author getAuthor();
}
Class-based Projections (DTOs)
PostInfo.java
Project Lombok provides an @Value annotation which makes the fields private final by default, and the class exposes a constructor that takes all fields and automatically gets equals(…) and hashCode() methods implemented.
package com.javachinna.model;
import lombok.Value;
@Value
public class PostInfo {
String title, authorName;
Long viewCount;
}
PostWithAuthorDTO.java
package com.javachinna.model;
import lombok.Value;
@Value
public class PostWithAuthorDTO {
private Post post;
private Author author;
}
Joining with JPQL
Join Unrelated Entities
Assume that we need to select both Post and Author entity with a single select query, then we can do so with the following JPA repository method.
@Query("select p as post, a as author from Post p inner join Author a on p.authorId = a.id where p.id = ?1")622
public PostWithAuthor getPostWithAuthor(Long id);
In the above JPQL query, we are using aliases post and author which should match with the accessor methods defined in the PostWithAuthor interface. So that JPA will map the result to the interface automatically. We are joining the Author entity using the inner join with on clause which was introduced in Hibernate 5.1.
Join Multiple Entities
Assume that we want to select data from multiple tables and map the result to a POJO, then we can use JPQL inner join with on clause to join the tables and JPA constructor expression to map the result to the POJO as follows
@Query("select new com.javachinna.model.PostInfo(p.title, a.firstName || ' ' || a.lastName, count(v)) from Post p inner join Author a on p.authorId = a.id inner join PageView v on p.slug = v.slug")
public List<PostInfo> getPostInfoWithConstrutorExp();
The class reference must be fully qualified and it must have a matching constructor. Hence, In the above query, we are using the fully qualified name of com.javachinna.model.PostInfo class followed by the new operator and this class is having a matching constructor exposed by lombok’s @Value annotation.
Join Unrelated Entities in JPA and Hibernate Older than 5.1
In JPA <=2.1 and Hibernate versions older than 5.1, entities should have an association to join them. Therefore, joining unrelated entities using the join clause is not supported.
However, we can still join unrelated entities using a Cartesian join or Cross join and reduce the cartesian product by specifying the conditions in the where clause. This is how we used to join the tables before the join clauses were introduced in SQL.
A Cartesian join or Cross join is a join of every row of one table to every row of another table. For example, if table A has 100 rows and is joined with table B, which has 1,000 rows, a Cartesian join will result in 100,000 rows.
@Query("select new com.javachinna.model.PostInfo(p.title, a.firstName || ' ' || a.lastName, count(v)) from Post p, Author a, PageView v where p.authorId = a.id and p.slug = v.slug")
public List<PostInfo> getPostInfoWithoutJoinClause();
For this JPQL query, Hibernate will generate the below cross join SQL query:
select post0_.title as col_0_0_, concat(author1_.first_name, ' ', author1_.last_name) as col_1_0_, count(pageview2_.id) as col_2_0_ from post post0_ cross join author author1_ cross join page_view pageview2_ where post0_.author_id=author1_.id and post0_.slug=pageview2_.slug
Note: It does not support
outer join. So, If you need outer join, then either you need to write a native query or upgrade your hibernate version.
Joining with HQL
In this section, we are going to implement the above Spring Data JPA examples using pure Hibernate.
Join Unrelated Entities
Here, we are using constructor expression for DTO projection since Hibernate doesn’t support interface-based projection.
public PostWithAuthorDTO getPostWithAuthor(Long id) {
String query = "select new com.javachinna.model.PostWithAuthorDTO(p, a) from Post p inner join Author a on p.authorId = a.id where p.id = ?1";
Session session = entityManager.unwrap(Session.class);
return session.createQuery(query, PostWithAuthorDTO.class).setParameter(1, id).getSingleResult();
}
Join Multiple Entities
public List<PostInfo> getPostInfoWithoutJoinClause() {
String query = "select new com.javachinna.model.PostInfo(p.title, a.firstName || ' ' || a.lastName, count(v)) from Post p, Author a, PageView v where p.authorId = a.id and p.slug = v.slug";
Session session = entityManager.unwrap(Session.class);
return session.createQuery(query, PostInfo.class).getResultList();
}
Join Unrelated Entities in Hibernate Older than 5.1
public List<PostInfo> getPostInfoWithoutJoinClause() {
String query = "select new com.javachinna.model.PostInfo(p.title, a.firstName || ' ' || a.lastName, count(v)) from Post p, Author a, PageView v where p.authorId = a.id and p.slug = v.slug";
Session session = entityManager.unwrap(Session.class);
return session.createQuery(query, PostInfo.class).getResultList();
}
Test with Junit 5
DemoApplicationTests.java
package com.javachinna.demo;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import com.javachinna.model.PostInfo;
import com.javachinna.model.PostWithAuthor;
import com.javachinna.model.PostWithAuthorDTO;
import com.javachinna.repo.PostInfoRepository;
import com.javachinna.repo.PostRepository;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private PostRepository postRepository;
@Autowired
private PostInfoRepository postInfoDAO;
@Test
public void getPostWithAuthorJpaTest() {
PostWithAuthor postWithAuthor = postRepository.getPostWithAuthor(1L);
Assertions.assertEquals("Chinna", postWithAuthor.getAuthor().getFirstName());
}
@Test
public void getPostInfoWithConstrutorExpJpaTest() {
List<PostInfo> list = postRepository.getPostInfoWithConstrutorExp();
Assertions.assertEquals(2, list.get(0).getViewCount());
}
@Test
public void getPostInfoWithoutJoinClauseJpaTest() {
List<PostInfo> list = postRepository.getPostInfoWithoutJoinClause();
Assertions.assertEquals(2, list.get(0).getViewCount());
}
@Test
public void getPostWithAuthorTest() {
PostWithAuthorDTO postWithAuthor = postInfoDAO.getPostWithAuthor(1L);
Assertions.assertEquals("Chinna", postWithAuthor.getAuthor().getFirstName());
}
@Test
public void getPostInfoWithoutJoinClauseTest() {
List<PostInfo> list = postInfoDAO.getPostInfoWithoutJoinClause();
Assertions.assertEquals(2, list.get(0).getViewCount());
}
@Test
public void getPostInfoWithConstrutorExpTest() {
List<PostInfo> list = postInfoDAO.getPostInfoWithConstrutorExp();
Assertions.assertEquals(2, list.get(0).getViewCount());
}
}
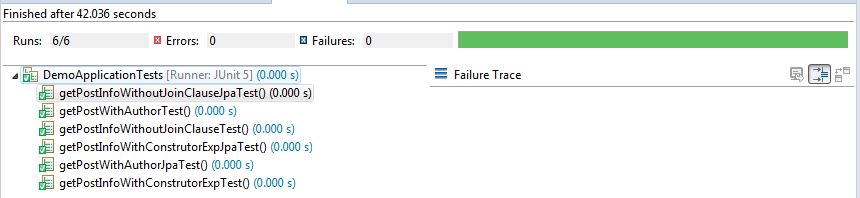
Test Result
References
https://docs.jboss.org/hibernate/orm/5.2/userguide/html_single/chapters/query/hql/HQL.html
https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa/docs/current/reference/html/#projections
https://thorben-janssen.com/how-to-join-unrelated-entities
Source Code
https://github.com/JavaChinna/spring-jpa-hibernate-join-unrelated-entities
Conclusion
That’s all folks. In this article, we have explored various approches for joining the results of multiple entities using Spring Data JPA and Hibernate.
Please share it in your circle if you like this article. Thanks for reading.



Would you develope appointment web project with doctors using java spring hibernate maven mysql ,
calendar,jquery css, project and published.
Due to time constraints, I can write articles/tutorials on specific topics only. It is very difficult to develop and publish a complete web application.
Thank you for this helpful article. What type of repo is PostRepository (CRUD, JPA, Custom) and does it have to specify both Author and Post in its declaration?
It is a JPARepository for the Post Entity. So you don’t need to specify Author in its declaration. You can have a look at the code yourself here.