Most Spring Tutorials available online teach you how to create/secure a Rest API with Spring boot. However, sometimes there will be specific use cases where you will need to create/secure REST API without using spring boot. This tutorial aims to help you create a REST application without using Spring Boot at all.
Note: If you don’t wanna use even the Spring framework, then you can read on how to create REST API in Java without Spring.
What you’ll build
A Spring REST service which will simply accept a name as a path variable in the request and say hello with that name in the response
What you’ll need
- Spring Tool Suite 4
- JDK 11
- MySQL Server 8
- Maven
Tech Stack
- Spring 5
- JDK 11
- Log4j 2
Bootstrap your application
Let’s bootstrap the application by creating a maven project in STS
Project Dependencies
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.javachinna</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-rest-jwt-demo</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-rest-jwt-demo Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<java-version>11</java-version>
<spring.version>5.2.3.RELEASE</spring.version>
<hibernate.version>5.4.1.Final</hibernate.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Web MVC -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Required for converting JSON data to Java object and vice versa -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.10.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet API -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>SpringRestJwt</finalName>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>${java-version}</source>
<target>${java-version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3</version>
<configuration>
<warSourceDirectory>src/main/webapp</warSourceDirectory>
<warName>SpringRestJwt</warName>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
Spring Configuration
SpringWebInitializer.java
WebApplicationContext can be configured using web.xml or Java-based configuration as shown below
SpringWebInitializer class extends Spring’s AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer to configure the WebApplicationContext.
package com.javachinna.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class SpringWebInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { WebConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
@Override
protected Class[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] {};
}
}
WebConfig.java
WebConfig class implements WebMvcConfigurer to configure the Jackson message converters
@EnableWebMvc annotation is used to enable Spring MVC support
@ComponentScan annotation is used with the @Configuration annotation to tell Spring the packages to scan for annotated components.
package com.javachinna.config;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@EnableWebMvc
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.javachinna")
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
converters.add(new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter());
}
}
Create REST Controller
GreetController.java
Controller class for exposing a GET REST API
package com.javachinna.controller;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class GreetController {
private Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(GreetController.class);
@GetMapping("/greet/{name}")
public String greet(@PathVariable String name, ModelMap model) {
String greet = "Hello!!! " + name + " How are You?";
logger.info(greet);
return greet;
}
}
Log4J Configuration
log4j.properties
# Root logger option
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout, file
# Redirect log messages to console
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.out
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
# Redirect log messages to a log file
log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
#outputs to Tomcat home
log4j.appender.file.File=${catalina.home}/logs/myapp.log
log4j.appender.file.MaxFileSize=5MB
log4j.appender.file.MaxBackupIndex=10
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
Build Application
Run mvn clean install command to clean and build the war file
Deploy Application
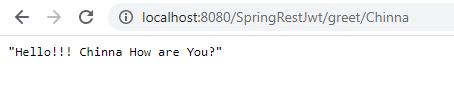
Deploy the generated war file in a server like tomcat and hit the URL http://localhost:8080/SpringRestJwt/greet/Chinna
Conclusion
That’s all folks. In this article, we have developed a simple Spring REST service without using Spring Boot. Thank you for reading
Read Next: Securing Spring REST services using JWT without using Spring Boot




Great tutorial.
Please where did you get to set your port to 8080?
The default port for tomcat server is 8080. So we don’t need to set it explicitly unless you wanna use a different port number. I have installed the tomcat server and deployed the war file in it. If you want to change the port number, then you can do so by following the below steps.
1) Locate server.xml in {Tomcat installation folder}\ conf \
2) Find following similar statement
<Connector connectionTimeout=”20000″ port=”8080″ protocol=”HTTP/1.1″ redirectPort=”8443″ />
3) Change the port “8080” to something else and save. Restart the server if it is already running
I hope it clarifies your query. Please let me know if more clarifications required.
Is it possible to use embedded Tomcat?
Yes. It is possible. I’ll publish a post on that shortly.
Here you go https://www.javachinna.com/2020/07/30/spring-rest-api-with-embedded-tomcat-without-using-spring-boot/
what is the folder structure of this project?
You can clone this project from GitHub and see the folder structure.